Gas Desulfurization
Hydrogen Sulfide Removal for Biogas Upgrading
H₂S Removal Technology Portfolio
DMT specializes in H₂S removal through a range of desulfurization technologies under the Sulfurex® umbrella. This includes a chemical process (Sulfurex®CR), a biological process (Sulfurex®BF), and a biological-chemical process (Sulfurex®BR). Each H₂S removal treatment method has its own specific advantages that if leveraged correctly, can help maximize a project’s ROI.
Technology Selection for H₂S Removal
There are various factors to consider when selecting the optimal technology for H₂S removal. These factors can be site conditions, gas application, operation & maintenance (O&M), capital expenditure (CAPEX) or operational expense (OPEX). Our sales team will be happy to assist during this selection process.
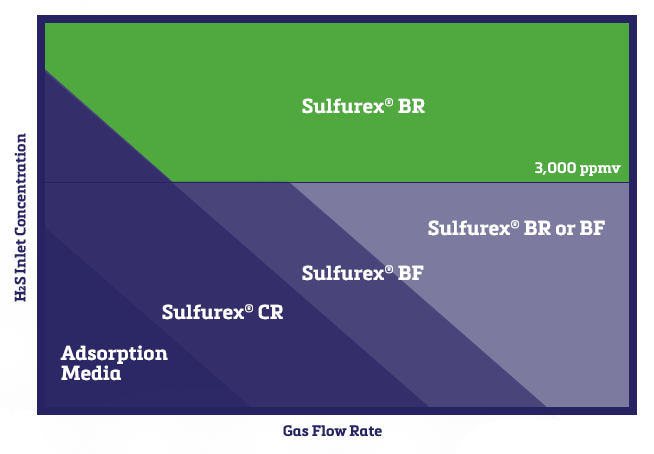
A helpful and main contributing factor will be the plant’s H₂S inlet concentration, of which it is particularly important to note the 3,000 ppmv line where a Sulfurex® BR would be most optimal compared to the Sulfurex® BF.

What is gas desulfurization (H₂S removal)?
Biogas is a mixture of gases produced by the breakdown of organic matter. Additionally, biogas is primarily methane (CH₄), carbon dioxide (CO₂), hydrogen sulfide (H₂S), water vapor, and other trace compounds (e.g., siloxanes). Using biogas as a renewable energy source requires pretreatment technologies to remove harmful contaminants present. Examples include H₂S and siloxanes.
Hydrogen Sulfide: a toxic gas
Hydrogen sulfide (H₂S) is a toxic gas that is colorless, flammable, extremely hazardous. H₂S causes a variety of issues:
- Firstly, H₂S poses health and safety risks. H₂S causes a wide range of health effects when breathing it. While the effects depend on how much H₂S you breathe and for how long, exposure to very high concentrations can quickly lead to death.
- Secondly, H₂S contributes to SOx emissions. H2S is a key component in the global sulfur cycle. It oxidizes in the atmosphere to sulfur dioxide (SO2), which can convert to sulfate through three different chemical pathways. H2S is not a climate change gas. However, because H2S can convert in the atmosphere to sulfate, it contributes to the cooling influence provided by atmospheric sulfate.
- Thirdly, H₂S is corrosive by nature. The presence of H₂S can lead to rapid and extensive damage of cogeneration engines and microturbine units. Treatment facilities, including electrical controls, instrumentation, process equipment, tankage and ventilation systems, are affected. Such corrosion results in costly, premature replacement or rehabilitation of systems reducing the overall lifecycle of a plant.
There is a high cost associated to H₂S removal technologies, predominantly based on chemical and physical processes. Therefore, biogas pretreatment contributes significantly to the overall operation and maintenance costs of any energy recovery system.
Gas Desulfurization (H₂S removal) Technologies
Common H₂S removal technologies for H₂S removal from biogas fall into one of the following:
- Absorption into a liquid either water or caustic solution,
- Adsorption on a solid such as iron oxide based materials or activated carbon, and
- Biological conversion by which sulfur compounds convert into elemental sulfur by sulfide oxidizing microorganisms with addition of air and oxygen.
DMT offers a wide portfolio for gas desulfurization tailored to a plant’s specification.
